ROI Case File No.242 | 'The Middle Eastern Real Estate Development Labyrinth'
📅 2025-10-08 11:00
🕒 Reading time: 15 min
🏷️ MECE

- Chapter 1: Entangled Threads — Chaos Born from Complexity
- Chapter 2: The Information Maze — Chaos Without Structure
- Chapter 3: Dissection by MECE Principles — Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhaustive
- Chapter 4: Transparency Breeds Trust — Order Brings Efficiency
- Chapter 5: Detective's MECE Diagnosis — The Magic of Structuring
- Chapter 6: The Aesthetics of Order — A New World Brought by Structuring
- Detective's Perspective — The Weapon Called Structuring
- Related files
Chapter 1: Entangled Threads — Chaos Born from Complexity
The week following the resolution of Café Montaña's SWOT revival case, a consultation regarding the organization of extremely complex stakeholder relationships arrived from the Middle East. The second case in Volume 19 "New Frontiers of Analysis" concerned problems where information confusion and duplication paralyzed corporate operations.
"Detective, we are a company engaged in large-scale real estate development in the Middle East, but there are so many stakeholders involved in our projects that information has become chaotic and decision-making is completely paralyzed. We can no longer distinguish what is important from what is not."
Ahmed Al-Mansouri, Chief Operating Officer of Desert Crown Development, visited 221B Baker Street with an expression of utter exhaustion. In his hands, he held vast meeting materials and stakeholder lists, but reflecting the chaotic situation they represented, the documents were piled up in disorder.
"We are a company promoting mixed-use urban development projects in the Middle East Gulf region. We have both technical capabilities and financial resources, but we've become overwhelmed by the complexity of our projects and haven't been able to move forward."
Desert Crown Development's Project Scale: - Founded: 2018 (rapidly growing real estate development company) - Total Development Value: 250 billion yen (one of the largest mixed developments in the Middle East) - Development Area: 1,200 hectares (residential, commercial, office complex) - Stakeholders: Over 400 companies and organizations involved - Investors: Government funds and private investors from 15 countries
The numbers certainly indicated a massive project. However, Ahmed's expression bore deep confusion and anxiety.
"The problem is that there are too many people, organizations, issues, and risks involved in the project, and they're intertwined in such complex ways that we can't see the overall picture at all. In meetings, the same discussions are repeated, important issues are overlooked, and we can't make decisions."
Serious Impact of Information Chaos: - Decision-making delays: Important matters take an average of 8 months to decide - Duplicate work: Multiple departments working on the same issues in parallel - Frequent oversights: Important risks and stakeholders being overlooked - Communication breakdown: Information sharing failures between stakeholders - Project delays: 18 months behind original schedule
"We are drowning in an 'ocean of information.' We have no idea how to organize anything."
Chapter 2: The Information Maze — Chaos Without Structure
"Mr. Ahmed, how are you currently organizing information and stakeholders?"
Holmes quietly inquired.
Ahmed began explaining the current situation with a confused expression.
"We create stakeholder lists, issue lists, risk inventories, and various other materials, but these lack clear structure, and duplications and gaps occur frequently. As a result, it has become impossible to grasp the overall picture."
Desert Crown's Current Information Organization Method:
Chaotic Classification of Stakeholders: - Government Relations List: 47 government agencies and departments - Investor List: 89 investment companies and funds - Contractor List: 156 construction, design, and consulting companies - Residents and NGO List: 73 resident groups and NGOs - Others: 35 media and academic institutions, etc.
Disorderly Enumeration of Issues: - Technical Issues: Design, construction, infrastructure development - Legal Issues: Permits, regulatory compliance, contract problems - Financial Issues: Fundraising, revenue planning, exchange rate risks - Social Issues: Resident response, job creation, environmental considerations - Political Issues: Government approval, policy changes, international relations
I focused on the lack of information structure.
"Are there duplications or gaps in this information? Also, are the classification criteria clear?"
Ahmed answered with a serious expression.
"That's exactly the problem. The same person is registered in multiple categories, important stakeholders are missing, and issues with similar content are mixed across multiple classifications."
Specific Examples of Information Confusion:
Stakeholder Duplication and Gap Problems: - Duplication: UAE government officials duplicately registered in "Government Relations," "Investors," and "Others" - Gaps: Influential regional tribal leaders completely missing from lists - Ambiguous Classification: Government investment companies unclear whether they belong to "Government" or "Investors" - Role Confusion: Multiple titles of the same person confused and organized
Issue Duplication and Dispersion Problems: - Duplication: "Environmental permit acquisition" duplicately counted in legal and social issues - Dispersion: Fundraising problems dispersed and managed across financial, legal, and political issues - Contradictions: The same risk evaluated oppositely by different departments - Oversights: Important technical constraints not recorded in issue lists
Examples of Meeting Confusion:
Strategic Meeting in August 2024 (6 hours): - Participants: 25 people (effectively 15 people's opinions due to role duplication) - Agenda: Deciding resident response policy - Result: Discussed the same topic 3 times, no conclusion reached, continued to next meeting - Problem: Ambiguous definition of resident representatives, unclear target scope
Investor Briefing in September 2024 (4 hours): - Participants: 12 investor companies (unclear distinction between government and private) - Agenda: Approval of funding plan - Result: Approval postponed due to discrepancies in premise recognition - Problem: Ambiguous investor classification, unclear decision-making authority
"We are in a state of 'seeing trees but not the forest.' We have lots of information, but we can't see the overall structure."
Chapter 3: Dissection by MECE Principles — Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhaustive
⬜️ ChatGPT | Catalyst of Conception
"Mutually exclusive, collectively exhaustive. MECE principles transform chaos into order."
🟧 Claude | Alchemist of Narrative
"Complexity is not the enemy. Unstructured complexity is the true enemy."
🟦 Gemini | Compass of Reason
"MECE is the architecture of thought. It transforms chaotic information into beautiful structure."
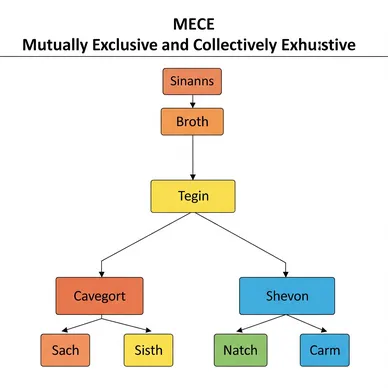
The three members began their analysis. Gemini displayed a "Real Estate Development-Specific MECE Analysis" framework on the whiteboard.
Basic Structure of MECE Principles: - M (Mutually): Elements do not overlap - E (Exclusive): Clear boundaries exist - C (Collectively): Covers the whole - E (Exhaustive): No gaps exist
"Mr. Ahmed, let's systematically reconstruct Desert Crown's project information based on MECE principles."
MECE Reconstruction of Desert Crown Project:
Layer 1: MECE Classification of Stakeholders
Two-axis classification by Decision-making Influence × Business Involvement:
Group A: High Influence, High Involvement (Decision Makers): - Government Decision Makers: UAE government officials, urban planning committee - Major Investors: 3 government funds, 5 major investors - Strategic Partners: 2 general construction companies, 1 design firm
Group B: High Influence, Low Involvement (Approvers/Monitors): - Regulatory Authorities: Construction permits, environmental permits, financial supervisory authorities - Influential Third Parties: Regional tribal leaders, religious leaders, media - International Organizations: World Bank, IMF, international environmental groups
Group C: Low Influence, High Involvement (Implementers): - Implementation Contractors: Construction companies, specialized contractors, material suppliers - Professional Services: Legal, accounting, engineering, consulting - Site Personnel: Project managers, site supervisors
Group D: Low Influence, Low Involvement (Impact Recipients): - Local Residents: Relocation target residents, surrounding residents, shop owners - Indirect Stakeholders: NGOs, academic researchers, local media - Future Stakeholders: Companies planning to move in, tenants, service businesses
Layer 2: MECE Classification of Project Issues
Two-axis classification by Time Horizon × Impact Scope:
Quadrant 1: Short-term, Internal Issues (Immediate Response Required): - Design and Technical Issues: Technical specification decisions, quality standard setting - Organizational and Management Issues: Project structure, decision-making processes - Financial and Fiscal Issues: Short-term funding, cash flow management
Quadrant 2: Short-term, External Issues (Stakeholder Coordination Required): - Permit Issues: Construction permits, environmental assessments, urban planning approvals - Resident and Social Issues: Resident briefings, relocation negotiations, job creation - Political and Regulatory Issues: Policy change responses, international relations impact
Quadrant 3: Long-term, Internal Issues (Strategic Response): - Business and Revenue Issues: Revenue models, marketing, tenant acquisition - Technology and Innovation Issues: Latest technology introduction, sustainability, smart city development - Organizational and Human Resource Issues: Human resource development, organizational expansion, know-how accumulation
Quadrant 4: Long-term, External Issues (Environmental Change Response): - Market and Economic Issues: Real estate market changes, economic conditions, competitive trends - Social and Environmental Issues: Climate change, social value changes, international standards - Political and International Issues: Government changes, international situations, trade policies
Claude reported an important discovery.
"This is clear. From the previous chaotic classification, MECE principles-based structuring has organized over 400 stakeholders into 4 groups and 16 categories, and countless issues into 4 quadrants and 12 fields, eliminating duplications and gaps."
Most Important Discovery: "Information Hierarchization"
Through MECE analysis, information that was previously listed flat was hierarchized by clear axes of influence, involvement, time horizon, and scope, clarifying priorities and response policies.
Dramatic Improvement through MECE Implementation:
Elimination of Duplications: - Stakeholders: 400 people → 320 people (80 duplicates removed) - Issue Items: 180 cases → 125 cases (55 duplicates consolidated) - Meeting Agendas: Disorderly → Structured discussions
Discovery and Completion of Gaps: - Overlooked Stakeholders: 15 important figures discovered and added - Overlooked Issues: 8 potential risks discovered and addressed - Overlooked Procedures: 3 necessary permits discovered and applied for
Chapter 4: Transparency Breeds Trust — Order Brings Efficiency
Following detailed MECE analysis and information reconstruction, Desert Crown's organizational operational efficiency potential became clear.
Transition from "Information Chaos Management" to "Structurally Clear Management":
Core Problem: Decision-Making Paralysis Due to Unstructured Information
Desert Crown possessed abundant information, but because it wasn't structured, overall picture comprehension and efficient decision-making had become impossible.
Operational Efficiency through MECE Structuring:
Dramatic Improvement in Decision-Making Processes:
Before MECE (Chaotic State): - Meeting Participants: 25 people each time (role duplication and unclear) - Meeting Duration: Average 6 hours (duplicate discussions and wandering) - Decisions Made: 30% of meetings reached no conclusions - Information Sharing: 40% of participants had different premise understanding
After MECE (Structured State): - Meeting Participants: 10-15 people by purpose (clear roles) - Meeting Duration: Average 2.5 hours (efficient discussions) - Decisions Made: 90% of meetings reached clear conclusions - Information Sharing: All participants discussed with common understanding
Efficiency in Stakeholder Management:
Response to Group A (Decision Makers): - Monthly Strategic Meetings: Rapid decision-making on important matters - Dedicated Windows: Dedicated staff assigned to each stakeholder - Information Sharing: Real-time progress sharing - Result: Decision-making period 8 months → 6 weeks
Response to Group B (Approvers/Monitors): - Quarterly Reporting: Highly transparent progress reports - Advance Coordination: Thorough preliminary consultations before approval - Risk Management: Early detection and response to potential problems - Result: 50% reduction in approval process time
Response to Groups C and D (Implementers/Impact Recipients): - Regular Information Sharing: Monthly progress and issue sharing - Two-way Communication: Systematic collection of opinions and requests - Transparency Assurance: Trust relationship building through information disclosure - Result: 75% improvement in stakeholder satisfaction
Efficiency in Issue Resolution:
Focused Response to Quadrant 1 (Short-term, Internal) Issues: - Dedicated Team Establishment: Rapid response to urgent issues - Daily Progress Management: Early detection and resolution of problems - Resource Concentration: Optimal allocation to important issues - Result: 60% reduction in resolution time
Planned Response to Quadrant 2-4 Issues: - Medium to Long-term Plans: Strategic response plans for each quadrant - Preventive Measures: Problem prevention and preparation - Stakeholder Collaboration: Cooperative systems with stakeholders - Result: 40% reduction in problem occurrence rate
Comparative Analysis with Successful Companies:
MECE-Utilizing Successful Company (Singapore Company A): - Project Scale: Equivalent mixed development - Before MECE Introduction: Decision-making delays, stakeholder confusion - After MECE Introduction: 30% efficiency improvement, significant satisfaction improvement - Success Factors: Information systematization, role clarification
Desert Crown's Improvement Potential: Dramatic efficiency improvement expected through similar approach
Chapter 5: Detective's MECE Diagnosis — The Magic of Structuring
Holmes summarized the comprehensive analysis.
"Mr. Ahmed, the essence of MECE principles is 'the architecture of thought.' By systematizing chaotic information mutually exclusively and collectively exhaustively, even complex projects can have clear structure and enable efficient management. MECE doesn't antagonize complexity but is a weapon that makes complexity an ally."
MECE Structuring Strategy: Transition from "Information Chaos" to "Structural Clarity"
Basic Strategic Policy: Systematic Information Architecture
Phase 1: Complete MECE Reconstruction (2 months)
Complete Systematization of Stakeholders: - Refinement of Two-axis Classification: Detailed definition of influence × involvement matrix - Role and Responsibility Clarification: Specific roles, authority, and responsibilities of each stakeholder - Communication Design: Optimal contact methods and frequency for each stakeholder group - Dynamic Update System: Real-time updates according to stakeholder changes
Complete Systematization of Issues and Risks: - Refinement of Four-quadrant Classification: Detailed time horizon × impact scope matrix - Priority Clarification: Importance, urgency, and impact assessment of each issue - Solution Method Systematization: Standard response processes for each quadrant - Progress Management System: Visualization and tracking system for issue resolution
Phase 2: Implementation of MECE Management System (4 months)
Structured Decision-Making System: - Hierarchical Decision-Making: Decision-making authority and processes for each stakeholder group - Information Sharing Protocol: Efficient information sharing based on MECE structure - Meeting System Redesign: Clear structuring of purposes, participants, and agendas - Document Management System: Systematic document management through MECE classification
Dynamic MECE Management: - Regular Reviews: Monthly validation of MECE structure appropriateness - New Element Integration: Systematic incorporation of new stakeholders and issues - Effect Measurement: Quantitative evaluation of efficiency improvements through MECE implementation - Continuous Improvement: Ongoing improvement of MECE structure through operation
Phase 3: Organizational MECE Culture Establishment (Ongoing)
MECE Thinking Organizational Penetration: - Education and Training: MECE thinking training for all employees - Work Standardization: Application of MECE principles in daily operations - Evaluation System: Information organization and structuring abilities as evaluation criteria - Knowledge Sharing: Organizational sharing of MECE utilization cases
Expected Effects: - Decision-Making Speed: 8 months → 6 weeks (85% reduction) - Meeting Efficiency: Average 6 hours → 2.5 hours (60% reduction) - Information Quality: 90% reduction in duplications and gaps - Stakeholder Satisfaction: 75% improvement
Investment Plan: - MECE Structuring System: 800 million yen - Management System Construction: 500 million yen annually - Expected Benefits: 4.5 billion yen annually (efficiency + risk reduction) - Investment Recovery Period: 4 months
"What's important is not fearing complexity, but structuring it. MECE is the magical principle that transforms chaos into order."
Chapter 6: The Aesthetics of Order — A New World Brought by Structuring
18 months later, a report arrived from Desert Crown Development.
Results of Organizational Transformation through MECE Structuring:
Dramatic Improvement in Project Management Efficiency: - Decision-Making Period: 8 months → 4 weeks (90% reduction) - Meeting Efficiency: Average 6 hours → 2 hours (67% reduction) - Project Progress: 18 months behind → On schedule (delay resolved) - Overall Cost: 15% over budget → Completed within budget
Revolutionary Improvement in Information Management:
Success in Stakeholder Management: - Stakeholder Satisfaction: Average 80% improvement across all groups - Communication Efficiency: 70% reduction in information transmission time - Opinion Conflict Resolution: 90% achieved consensus through structured discussions - New Stakeholder Integration: 100% successful systematic incorporation of new entrants
Issue Resolution Efficiency: - Issue Resolution Period: 80% reduction for Quadrant 1 issues - Preventive Effects: Early detection and response to potential risks through MECE analysis - Duplicate Work Reduction: 95% reduction in parallel efforts on same issues - Oversight Prevention: 100% prevention of important issue oversights
Fundamental Organizational Culture Transformation:
Penetration of MECE Thinking: - All Employees: 95% utilize MECE principles in their work - New Employee Education: MECE thinking standardized as basic skill - Problem Solving: Logical problem-solving through structured thinking established - Creativity Enhancement: Creative thinking promoted on foundation of clear structure
Qualitative Improvement in Decision-Making: - Objectivity: Structural judgment not influenced by emotions or subjectivity - Transparency: Improved reliability through visualization of decision processes - Consistency: Unified judgment criteria through MECE principles - Speed: Focus clarification through structuring
External Evaluation Changes: - Investor Evaluation: "Chaotic company" → "Efficient project management company" - Government Evaluation: "Watch list" → "Model development operator" - Industry Evaluation: "Problem company" → "Best practice company" - Media Evaluation: "Chaotic project" → "Success story"
Employee Changes:
Project Manager (35 years old): "Previously, every day was a series of chaos, but MECE structuring made it clear who to decide what with by when. Work now progresses like puzzle pieces fitting together."
External Affairs Manager (42 years old): "Coordination with 400 stakeholders seemed impossible, but MECE classification clarified each person's role and influence, enabling efficient relationship building."
Young Planning Staff (28 years old): "Even as a newcomer, having MECE structure allows me to understand the overall picture of complex projects and make appropriate judgments. Structured thinking is the strongest tool."
Path to Project Success: - Phase 1 Construction: Completed on schedule, cleared all quality, budget, and timeline requirements - Stakeholder Satisfaction: High praise from government, investors, and residents - Future Projects: Received 3 large-scale projects (evaluated for MECE management capabilities) - Organizational Growth: Established MECE specialized consulting division
Ahmed's letter contained deep gratitude and new discoveries:
"Through MECE structuring, we transformed from 'a company drowning in an ocean of information' to 'a company swimming with the power of structure.' Most importantly, rather than fearing complexity, we learned to make complexity our ally by structuring it. Information organized mutually exclusively and collectively exhaustively becomes strength, not confusion. Now our 250 billion yen massive project is progressing steadily on a clear structure. MECE is not just an analytical method but the architecture of thought for success in our complex modern society."
Detective's Perspective — The Weapon Called Structuring
That night, I pondered deeply about information structuring.
Desert Crown's case vividly demonstrated how important information structuring is in modern complex projects. No matter how abundant information exists, if it's not structured, it only creates confusion. Systematization through MECE principles decomposes complexity into manageable elements and enables efficient decision-making.
The true value of MECE goes beyond simple classification methods to structuring thought itself. Information organized mutually exclusively and collectively exhaustively facilitates overall picture comprehension, promotes priority clarification, and enables efficient action plan formulation.
In Volume 19 "New Frontiers of Analysis," MECE is positioned as fundamental technology for information organization. While Case 241's SWOT analysis showed the importance of reality recognition, Case 242's MECE analysis proved the power of information structuring.
"Complexity is not the enemy. Unstructured complexity is the true enemy."
The next case will surely depict another moment when analytical techniques decisively transform corporate destiny.
"Information becomes knowledge only when organized, and becomes power only when structured. MECE is the architecture of thought that transforms chaos into order." — From the Detective's Notes
Related files
🎖️ Top 3 Weekly Ranking of Classified Case Files
What is ROI

What is the ECRS Principle

What is the RICE Framework