ROI 【🔏CLASSIFIED CASE FILE】 No. 008 | What is PEST Analysis
📅 2025-05-22
🕒 Reading time: 6 min
🏷️ PEST Analysis 🏷️ Learning 🏷️ 【🔏CLASSIFIED CASE FILE】
- What is PEST Analysis - Case Overview
- Basic Structure of PEST Analysis - Evidence Analysis
- PEST Analysis Implementation Procedure - Investigation Methods
- The Power of PEST Analysis - Hidden Truths
- PEST Analysis Limitations and Precautions - Potential Dangers
- PEST Analysis Evolution and Related Methods - Related Case Files
- Conclusion - Investigation Summary
Detective's Note: A four-letter cipher "PEST Analysis" frequently witnessed in strategic planning rooms and executive meetings. External environment analysis depicted by the initials Political, Economic, Social, Technological is positioned as an important method for visualizing "invisible forces" in corporate strategic planning. However, reports continue that many organizations remain at "formal environmental surveys" with insufficient utilization for actual strategic planning and decision-making. Determine the identity of this macroscopic analytical method and the structural problems behind why many companies end with "analyze and be satisfied."
What is PEST Analysis - Case Overview
PEST Analysis (Political/Economic/Social/Technological), external environment analysis covering "political-economic-social-technological" factors. This fundamental framework for external environment analysis was reportedly proposed by Harvard Business School management scholar Francis Aguilar in the 1960s. It's recognized among our clients as a method for systematically organizing external factors that companies cannot control through their own power and utilizing them for strategic planning. However, in actual workplaces, it's often used as a "framework for information gathering," with the original purpose of applying analytical results to strategy frequently being lost.
Investigation Memo: Structuring external environment through four perspectives. Possesses the power to capture "invisible currents" surrounding companies and predict future opportunities and threats. However, there's a mystery that in many cases, it ends with information listing, with insufficient elevation to insights.
Basic Structure of PEST Analysis - Evidence Analysis
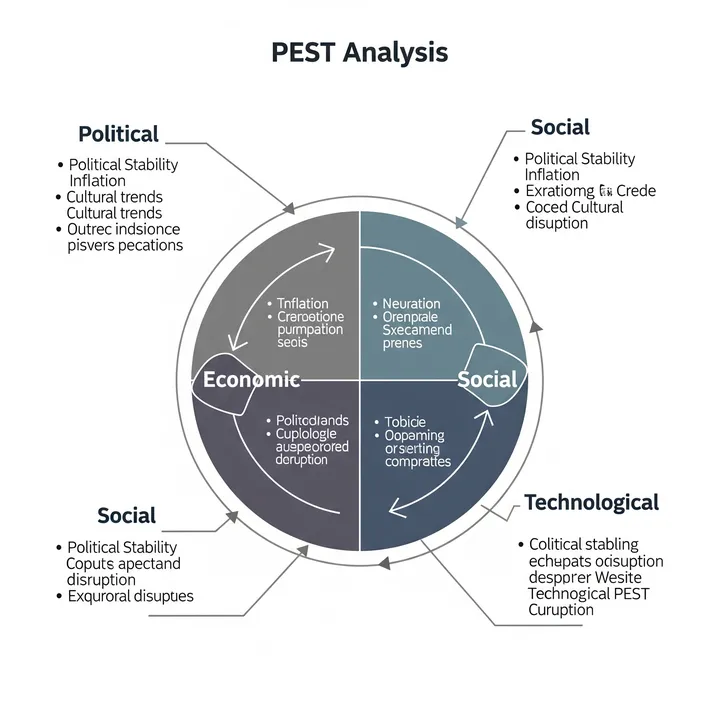
Primary Evidence: The Four Domains of PEST
Political - Political/Legal Environment
"Impact of government/politics on companies"
・Political system/policy direction changes
・Law/regulation establishment/revision/abolition
・Tax systems/subsidies/preferential measures
・Political stability/international relations
・Industry regulations/entry barrier changes
Economic - Economic Environment
"Impact of economic conditions on companies"
・GDP growth rate/economic trends
・Interest rates/exchange rates/inflation rates
・Employment situation/wage levels
・Consumer disposable income
・Capital markets/investment environment
Social - Social/Cultural Environment
"Impact of social/cultural changes on companies"
・Demographics/declining birthrate/aging population
・Lifestyle/value changes
・Education level/health consciousness
・Work style/consumption behavior changes
・Social issues/environmental awareness
Technological - Technological Environment
"Impact of technological innovation on companies"
・Emergence/proliferation of new technologies
・R&D trends
・Digitalization/automation progress
・Patents/intellectual property rights
・Technology lifecycles
Evidence Analysis: PEST Analysis' excellence lies in reframing analysis that tends toward internal company factors through relationships with external environment. It particularly possesses a structure enabling early detection of long-term environmental change signs and strategic preparation.
PEST Analysis Implementation Procedure - Investigation Methods
Investigation Finding 1: Concrete PEST Analysis Example (Electric Vehicle Manufacturer Case)
Case Evidence:
Political Factors:
・EV preferential policies by country (subsidies/tax benefits)
・ICE vehicle sales ban timeline setting
・Environmental regulation strengthening (CO2 emission standards)
・Autonomous driving legal framework status
・Trade friction/tariff policy impacts
Economic Factors:
・Oil price fluctuations and gasoline prices
・Lithium and other battery material prices
・Interest rate trends and capital investment impacts
・Consumer purchasing power changes
・Semiconductor shortage production cost increases
Social Factors:
・Rising environmental consciousness
・Youth car-sharing preferences
・Urban car-离れ trends
・Mobility needs changes due to aging
・Lifestyle digitalization
Technological Factors:
・Battery technology advances
・Charging infrastructure expansion
・Autonomous driving technology development
・AI/IoT technology automotive applications
・Renewable energy technology
Investigation Finding 2: Impact Degree Analysis of Each Factor
Impact Assessment Perspectives:
Time Horizon Classification:
・Short-term impact (1-2 years): Subsidy policies, oil prices
・Medium-term impact (3-5 years): Charging infrastructure, technology adoption
・Long-term impact (5-10 years): Social values, technological innovation
Impact Direction:
・Opportunity factors: Environmental regulation strengthening, technological progress
・Threat factors: Material price increases, competitor entry
・Dual-nature factors: Digitalization, value changes
Impact Quantification:
・High impact: 20%+ variation in sales/profits
・Medium impact: 10-20% variation
・Low impact: Under 10% variation
Investigation Finding 3: Strategic Planning Utilization - Examining strategic options leveraging opportunity factors - Planning countermeasures/risk hedging for threat factors - Multiple pattern assumptions in scenario planning - Utilizing as basis for investment priority decisions
The Power of PEST Analysis - Hidden Truths
Critical File 1: External Environment Sensitivity Enhancement Effect of directing management attention, which tends toward internal factors, to external environment. Improves ability to systematically capture easily overlooked environmental change signs.
Critical File 2: Long-term Strategy Foundation Building Provides foundation for strategic planning considering medium to long-term environmental changes in management often pursued by short-term performance. Becomes basis for advance investment judgments.
Critical File 3: Risk Management Systematization Provides framework for recognizing and managing high-uncertainty external environment changes as risks. Enables competitive advantage acquisition through proactive response.
Critical File 4: Common Language with Stakeholders Functions as common analytical framework in strategic discussions with investors, partners, government agencies, etc. Contributes to accountability and persuasiveness improvement.
PEST Analysis Limitations and Precautions - Potential Dangers
Warning File 1: Information Gathering Termination Syndrome Most frequent problem. Cases where satisfaction comes from organizing information across four domains, with insufficient utilization for strategic planning. Risk of falling into "analysis for analysis' sake."
Warning File 2: Overlooking Inter-factor Interactions Possibility of overlooking complex impacts and synergy effects between factors by analyzing each factor independently. Real environmental changes are more complex and dynamic.
Warning File 3: Qualitative Analysis Limitations Many factors remain qualitative information, making quantitative impact measurement and prioritization difficult. Specific guidance for strategic judgment tends to become unclear.
Warning File 4: Static Snapshot Trap Remaining at environmental analysis at one point in time, with insufficient continuous environmental change monitoring. Responsiveness to dynamic environmental changes doesn't improve.
Warning File 5: Ignoring Regional/Industry Characteristics Risk of overlooking specific regional or industry-unique environmental factors by biasing toward global generalizations. Uniform analysis reduces effectiveness.
PEST Analysis Evolution and Related Methods - Related Case Files
Related Evidence 1: PESTEL Analysis (Adding Environmental + Legal)
Environment: Climate change, environmental regulations, sustainability
Legal: Independence of legal aspects from Political
More detailed external environment analysis possible
Related Evidence 2: STEEP Analysis (Adding Social + Ethical)
Social → Socio-cultural
Ethical: Corporate ethics, CSR, ESG factors
Reflecting increased importance of moral/ethical aspects
Related Evidence 3: Integration with Scenario Planning
Multiple scenario construction based on PEST Analysis results
・Optimistic scenario, pessimistic scenario, realistic scenario
・Strategic option examination for each scenario
・Improved responsiveness to uncertainty
**Related Evidence 4: Integration with SWOT Analysis **
PEST → External environment analysis → SWOT O(Opportunities)・T(Threats)
Integrated utilization of internal and external analysis
Achieving more comprehensive strategic analysis
Related Evidence 5: KPI/Early Warning Systems
Indicator-izing monitoring of important PEST factors
・Policy trend watching
・Regular economic indicator monitoring
・Technology trend analysis
・Continuous environmental change understanding
Conclusion - Investigation Summary
Detective's Final Report:
PEST Analysis is "a compass for reading the massive currents of external environment." Structuring through four perspectives - Political, Economic, Social, Technological - possesses the power to organize complex and uncertain external environments into comprehensible form.
The most important discovery in this investigation was that PEST Analysis' true value lies not in "information gathering" but in "utilization for strategic planning." The "analyze and be satisfied" syndrome seen in many organizations wastes the essential value of this method. "What to do next" after identifying environmental factors becomes the source of competitive advantage.
It also became clear that PEST Analysis should be utilized as a "dynamic monitoring system" rather than "static analysis." By utilizing it for continuous environmental change monitoring and strategy modification rather than one-time analysis, it demonstrates true value.
Furthermore, the importance of considering inter-factor interactions and complex impacts was highlighted. Real environmental changes often occur through combinations of multiple factors rather than single factors. Through integration with scenario planning and SWOT Analysis, more three-dimensional strategic analysis becomes possible.
PEST Analysis is certainly not a "universal prediction tool." However, in an era of high uncertainty, its value as a foundation for enhancing external environment sensitivity and promoting strategic thinking is immeasurable.
External Environment Analysis Maxim: "Excellent strategy means early detection of invisible environmental change signs and converting them into competitive advantages."
Case Closed
Solve Your Business Challenges with Kindle Unlimited!
Access millions of books with unlimited reading.
Read the latest from ROI Detective Agency now!
*Free trial available for eligible customers only