ROI【🔏CLASSIFIED CASE FILE】 No. X019 | What is BSC (Balanced Scorecard)
📅 2025-06-19
🕒 Reading time: 8 min
🏷️ BSC 🏷️ Learning 🏷️ 【🔏CLASSIFIED CASE FILE】
- What is BSC (Balanced Scorecard) - Case Overview
- Basic Structure of BSC - Evidence Analysis
- BSC Implementation Process - Investigation Methods
- The Power of BSC - Hidden Truths
- Limitations and Cautions of BSC - Potential Dangers
- Evolution and Related Methods of BSC - Related Case Files
- Conclusion - Investigation Summary
Detective's Note: A three-letter cipher revered in boardrooms and strategic planning departments - "BSC (Balanced Scorecard)." This strategic management system, developed by Harvard Business School's Robert Kaplan and David Norton in the 1990s, allegedly possesses the power to visualize corporate strategic objectives through four perspectives: Financial, Customer, Internal Business Process, and Learning & Growth. However, reports consistently indicate that many companies fall into states of "merely classifying KPIs into four categories" or "creating and finishing with satisfaction," failing to demonstrate the true power as a strategic execution tool. Why these four perspectives? We must uncover the mechanism that goes beyond listing numerical targets to promote actual corporate transformation.
What is BSC (Balanced Scorecard) - Case Overview
BSC (Balanced Scorecard) - a strategic management system jointly developed by Harvard Business School Professor Robert Kaplan and consultant David Norton in the early 1990s. Recognized among our clients as a comprehensive framework that breaks away from traditional finance-centered performance evaluation to set, measure, and manage corporate strategic objectives through four perspectives: Financial, Customer, Internal Business Process, and Learning & Growth. However, in actual practice, most companies use it superficially as a "KPI classification tool," with the majority unable to fully demonstrate its original function of connecting strategy to execution.
Investigation Memo: Strategic structuring and causal relationship visualization through four perspectives. Seemingly complex, yet behind this lies clear design philosophy: "balancing short-term financial results with long-term value creation" and "promoting strategy sharing and execution." We must uncover why these four perspectives and the mechanism for converting strategy into execution.
Basic Structure of BSC - Evidence Analysis
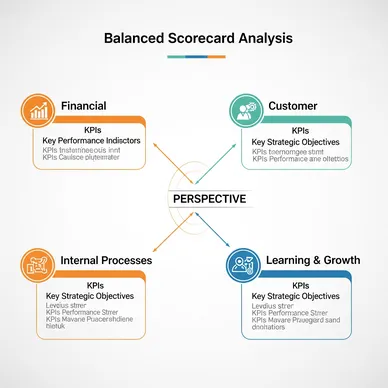
Primary Evidence: The Four Perspectives of BSC
Financial Perspective
"Financial results for shareholders and investors"
・Revenue, revenue growth rate
・Profit margin, ROI, ROE
・Cash flow, capital efficiency
・Shareholder value, enterprise value enhancement
・Cost reduction, productivity improvement
Customer Perspective
"Value delivery and results for customers"
・Customer satisfaction, customer loyalty
・Market share, customer acquisition rate
・Customer retention rate, customer lifetime value
・Brand recognition, reputation
・New customer acquisition, existing customer deepening
Internal Business Process Perspective
"Efficiency of internal processes supporting value creation"
・Quality, delivery time, cost, safety
・Innovation, new product development
・Manufacturing, sales, service delivery processes
・Business efficiency, automation, digitalization
・Risk management, compliance
Learning & Growth Perspective
"Organizational capabilities, talent, and technology supporting future growth"
・Employee satisfaction, engagement
・Skills, capability development, training
・Organizational culture, value penetration
・Information systems, technology infrastructure
・Knowledge management, knowledge accumulation
Evidence Analysis: The brilliance of BSC lies in the four perspectives being connected through hierarchical causal relationships. The structure is clearly designed so that long-term organizational capability strengthening ultimately connects to financial results through the flow: Learning & Growth → Internal Process → Customer → Financial.
BSC Implementation Process - Investigation Methods
Investigation Discovery 1: Concrete BSC Construction Example (Manufacturing Company)
Case Evidence (Automotive Parts Manufacturer Strategic Objectives):
Financial Perspective:
Objective: "Achieve 20% revenue increase and 12% operating margin in 3 years"
KPIs: Revenue growth rate, operating margin, ROE, cash flow
Initiatives: New market development, high-value product development, cost reduction
Customer Perspective:
Objective: "Customer satisfaction improvement and new customer acquisition"
KPIs: Customer satisfaction, delivery compliance rate, quality complaint rate, new orders
Initiatives: Quality improvement, delivery time reduction, technical proposal capability enhancement
Internal Business Process Perspective:
Objective: "Production efficiency improvement and innovation creation"
KPIs: Production efficiency, defect rate, new product development period, patent applications
Initiatives: IoT introduction, automation promotion, R&D investment expansion
Learning & Growth Perspective:
Objective: "Human resource strengthening and organizational capability enhancement"
KPIs: Employee satisfaction, training hours, engineer ratio, IT investment amount
Initiatives: Talent development programs, IT infrastructure development, corporate culture reform
Investigation Discovery 2: Causal Relationship Visualization through Strategy Maps
Strategy Map Chain Example:
Learning & Growth → Internal Process:
"Engineer skill improvement" → "New product development capability strengthening"
"IT infrastructure development" → "Production efficiency improvement"
"Corporate culture reform" → "Quality consciousness improvement"
Internal Process → Customer:
"New product development capability" → "Customer value enhancement"
"Production efficiency improvement" → "Cost competitiveness strengthening"
"Quality improvement" → "Customer satisfaction improvement"
Customer → Financial:
"Customer satisfaction improvement" → "Customer retention and repeat increase"
"New customer acquisition" → "Revenue expansion"
"Price competitiveness" → "Profit margin improvement"
Ultimate Causal Relationship:
"Human resource development investment" → "Technology capability improvement" → "Product competitiveness"
→ "Customer satisfaction" → "Revenue and profit growth"
Investigation Discovery 3: Implementation Steps
Step 1: Vision and Strategy Clarification
・Reconfirmation of corporate philosophy and vision
・Medium to long-term strategy formulation and sharing
・Priority issue and strategic theme identification
Step 2: Strategy Map Creation
・Strategic objective setting from four perspectives
・Organization of causal relationships between objectives
・Strategic story construction
Step 3: KPI and Target Value Setting
・Measurement indicator selection for each strategic objective
・Target value and deadline setting
・Responsibility and department clarification
Step 4: Action Plan Formulation
・Specific initiative and approach planning
・Budget and resource allocation
・Execution schedule formulation
Step 5: Operation and Monitoring
・Regular progress monitoring and evaluation
・Problem and challenge identification and countermeasures
・Strategy and objective review and adjustment
The Power of BSC - Hidden Truths
Alert File 1: Bridge Between Strategy and Execution By converting abstract strategy into concrete KPIs and initiatives, enables organization-wide strategy sharing and implementation in feasible form. Prevents "strategic failure" and connects to actual results creation.
Alert File 2: Balanced Management By including not only financial indicators but also customer, process, and learning perspectives, ensures balance between short-term results and long-term value creation. Enables construction of sustainable corporate growth foundation.
Alert File 3: Strategic Understanding Through Causal Relationships By clarifying causal relationships among four perspectives, enables organization-wide understanding and sharing of "why that initiative is important" and "how it connects to results."
Alert File 4: Continuous Improvement Promotion Through regular monitoring and review, enables continuous strategic improvement incorporating PDCA cycles. Functions as mechanism to improve adaptability to environmental changes.
Limitations and Cautions of BSC - Potential Dangers
Alert File 1: KPI Setting Becomes Purpose Most frequent problem. Cases where BSC creation itself becomes the purpose, satisfied with classifying KPIs into four perspectives. Risk of insufficient coordination with strategy execution and results creation.
Alert File 2: Causal Relationship Oversimplification Limitations of trying to explain complex business reality through linear causal relationships of four perspectives. Actual business is more complex and dynamic, with many elements that cannot be captured by simple causal relationships.
Alert File 3: Quantification Difficulties Particularly in Learning & Growth perspective, many elements are difficult to measure quantitatively. Risk of setting non-essential indicators through forced quantification.
Alert File 4: Static System Limitations Risk of operating established BSC statically, delaying response to environmental changes or strategic shifts. Particularly potential inability to respond to rapid changes in digital era.
Alert File 5: Increased Organizational Load Cases where excessively detailed KPI setting or frequent reporting increases field workload, adversely affecting core business. Risk of falling into "management for management's sake."
Evolution and Related Methods of BSC - Related Case Files
Related Evidence 1: Digital Era BSC Evolution
・Real-time dashboard visualization
・Prediction and analysis through AI and machine learning
・Agile management adaptation
・Addition of ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) perspective
・Stakeholder capitalism adaptation
Related Evidence 2: Integration with OKR (Objectives and Key Results)
BSC (Strategic Level) + OKR (Execution Level):
・Strategic objective setting through BSC for medium to long-term
・Quarterly concrete objective development through OKR
・Higher-speed [PDCA](../../BEHIND_CASE_FILES/ARTICLES/X003_PDCA) cycle realization
・Agile objective management at field level
Related Evidence 3: Coordination with 3C Analysis and SWOT Analysis
Strategic Analysis → BSC Construction flow:
・Market environment and competitive situation understanding through [3C analysis](/behind_case_files/articles/X016_3C)
・Company strength and challenge identification through SWOT analysis
・BSC design based on strategic planning
・Consistent flow from analysis to execution
Related Evidence 4: Combination with KPT
BSC Operation Reflection:
Keep: Well-functioning KPIs and initiatives
Problem: Problematic KPIs and initiatives
Try: New improvement measures to attempt
Regular review and improvement cycles
Related Evidence 5: Development to Individual BSC and Departmental BSC
Corporate BSC → Departmental BSC → Individual BSC:
・Hierarchical strategy development
・Coordination of company-wide and individual objectives
・Organization-wide strategic execution
・Individual contribution visualization
Conclusion - Investigation Summary
Final Investigator Report:
BSC (Balanced Scorecard) represents "a management compass that converts strategy into execution." Over 30 years have passed since Robert Kaplan and David Norton developed it in the 1990s, yet its value as a comprehensive strategic management system through four perspectives—Financial, Customer, Internal Process, and Learning & Growth—remains undiminished.
The most impressive aspect of this investigation was the excellence of BSC's "causal relationship design." By drawing clear strategic stories where investment in Learning & Growth improves Internal Processes, which connects to Customer value enhancement, ultimately generating Financial results, enables organization-wide understanding and sharing of "why that initiative is important." This represents a powerful mechanism for strategy understanding and execution promotion beyond mere KPI management.
However, the trap many companies fall into—"KPI setting becomes the purpose"—also emerged clearly. Cases frequently occur where satisfaction with classifying KPIs into four perspectives leads to insufficient coordination with actual strategy execution and results creation. BSC's true value lies not in "creating" but in "operating" and "continuously improving."
The "necessity for evolution" in the digital age also became apparent. Response to elements unimaginable in the 1990s—real-time dashboards, AI analysis, agile management, ESG perspectives—is now required. However, the value of BSC as a fundamental thinking framework remains unchanged.
Integrated utilization with other strategic analysis methods was also an important discovery. Formulating strategy through 3C analysis and SWOT analysis, managing execution through BSC, and reflecting through KPT analysis. This series of flows enables construction of consistent strategic management systems from analysis through execution to improvement.
The most important discovery is that BSC is not a "measurement tool" but a "transformation tool." Through strategic visualization from four perspectives and causal relationship clarification, it possesses the power to promote organizational behavioral change and realize actual corporate transformation. This represents the true power of this strategic management system.
Strategic Execution Maxim: "Superior strategy is understood and shared organization-wide, converted into concrete actions, and continuously improved."
Case Closed