ROI【🔏CLASSIFIED CASE FILE】 No. X024 | What is MECE
📅 2025-06-24
🕒 Reading time: 9 min
🏷️ MECE 🏷️ Learning 🏷️ 【🔏CLASSIFIED CASE FILE】
- What is MECE - Case Overview
- Basic Structure of MECE - Evidence Analysis
- MECE Implementation Process - Investigation Methods
- The Power of MECE - Hidden Truths
- Limitations and Cautions of MECE - Potential Dangers
- Applications and Related Methods of MECE - Related Case Files
- Conclusion - Investigation Summary
Detective's Note: A four-letter cipher revered in consulting and business analysis - "MECE." This logical thinking principle, formed by the initials of Mutually Exclusive and Collectively Exhaustive, appears as a simple concept of "comprehensive without gaps or overlaps," yet reigns as a powerful thinking technology for structuring complex problems and deriving accurate solutions. However, reports consistently indicate that many people understand it superficially as "just classify things," failing to demonstrate the original power of true logical structuring and insight generation. Why is eliminating "gaps" and "overlaps" important? We must uncover the true identity of the logical structuring mechanism and how this simple principle dramatically improves business analysis accuracy and persuasiveness.
What is MECE - Case Overview
MECE (Mutually Exclusive and Collectively Exhaustive) - systematized at McKinsey & Company in the 1960s as a fundamental principle of logical thinking. Recognized among our clients as a thinking technology that enables structuring and accurate analysis of complex problems by classifying and organizing information "comprehensively (Collectively Exhaustive)" and "without overlaps (Mutually Exclusive)." However, in actual practice, most cases apply it mechanically as "classification work for its own sake," losing sight of the original purposes of logical structure understanding and insight generation.
Investigation Memo: Logical structuring through elimination of gaps and overlaps. Seemingly obvious, yet behind this lies deep thinking technology: "accurately grasping the whole and analyzing efficiently." We must uncover why this principle is important and the mechanism for insight generation beyond simple classification.
Basic Structure of MECE - Evidence Analysis
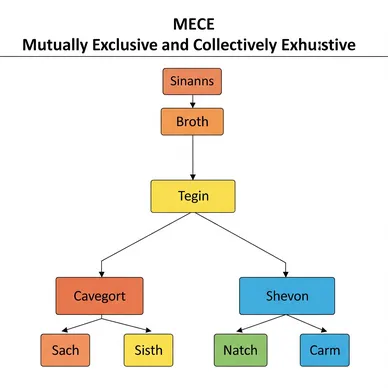
Primary Evidence: The Two MECE Principles
Mutually Exclusive
"State where no overlaps or duplications exist between elements"
・Each element is independent
・No single phenomenon belongs to multiple classifications
・Prevents double-counting due to overlaps
・Improves analysis accuracy and efficiency
Example: Age-based classification
✓ Good example: Teens, 20s, 30s, 40s and above
✗ Bad example: Teens, 20-30s, 30s and above (30s overlap)
Collectively Exhaustive
"State that comprehensively covers the entire scope"
・All elements are included
・Complete coverage of entire analysis target
・Prevents analysis errors due to oversights
・Enables comprehensive understanding and judgment
Example: Customer satisfaction classification
✓ Good example: Satisfied, Neutral, Dissatisfied
✗ Bad example: Satisfied, Dissatisfied (neutral customers missing)
MECE Classification Methods
Classification by Perspective
Time axis: Past, Present, Future
Spatial axis: Domestic, International
Subject axis: Individual, Corporate
Scale axis: Large, Medium, Small
Stage axis: Planning, Execution, Evaluation
Process-based Classification
Business process: Procurement → Manufacturing → Sales → Service
Decision process: Awareness → Consideration → Decision → Execution
Customer process: Acquisition → Activation → Retention → Expansion
Factor-based Classification
Internal factors, External factors
Direct factors, Indirect factors
Short-term factors, Long-term factors
Quantitative factors, Qualitative factors
Evidence Analysis: The brilliance of MECE lies in simultaneously eliminating thinking "gaps" and "waste," enabling the most efficient and accurate analysis with limited time and resources. Despite being a simple principle, it incorporates structure that dramatically improves logical thinking precision.
MECE Implementation Process - Investigation Methods
Investigation Discovery 1: Concrete MECE Analysis Example (Sales Decline Factor Analysis)
Case Evidence (Retail Industry Sales Decline Problem):
Problem: 20% year-over-year sales decline cause analysis
MECE Classification 1 (By Sales Components):
Sales = Customer Count × Average Spending per Customer
・Customer count decline: -15%
・Average spending decline: -5%
→ Customer count decline identified as main factor
MECE Classification 2 (By Customer Count Decline Factors):
Customer Count = New Customers + Existing Customers
・New customers: -30%
・Existing customers: -10%
→ New customer decline identified as serious issue
MECE Classification 3 (By New Customer Decline Factors):
Classified by Internal factors and External factors
Internal factors:
・30% advertising budget reduction
・New product launch delays
・Store staff service quality decline
External factors:
・Competitor store opening (within 5-minute walk)
・Foot traffic changes due to station area redevelopment
・Post-COVID consumption behavior changes
MECE Classification 4 (By Improvement Feasibility):
Classified by Immediate, Medium-term, Long-term
Immediate (within 1 month):
・Advertising enhancement
・Customer service training
・Pricing review and promotions
Medium-term (3-6 months):
・New product/service development
・Store layout improvement
・Digitalization and e-commerce strengthening
Long-term (1+ years):
・Location strategy review
・Business model transformation
・Brand reconstruction
Investigation Discovery 2: MECE Application in Strategic Planning
Case Evidence (New Business Entry Strategy):
Problem: Which new business field should we enter?
MECE Classification 1 (Overall Business Opportunity Overview):
Existing Market/New Market × Existing Product/New Product
・Existing Market × Existing Product: Market penetration strategy
・Existing Market × New Product: Product development strategy
・New Market × Existing Product: Market development strategy
・New Market × New Product: Diversification strategy
MECE Classification 2 (Detailed Diversification Strategy Analysis):
Related diversification and Unrelated diversification
Related diversification:
・Technology-related: AI, IoT fields
・Market-related: Adjacent industries
・Value chain-related: Upstream/downstream integration
Unrelated diversification:
・Growth fields: Healthcare, Environment
・Stable fields: Infrastructure, Public sector
・Profitable fields: Real estate, Finance
MECE Classification 3 (By Entry Method):
In-house development, M&A, Partnerships
In-house development:
・Advantages: Complete control, core technology accumulation
・Disadvantages: High time and risk
M&A:
・Advantages: Speed, existing customer/technology acquisition
・Disadvantages: High cost, integration risks
Partnerships:
・Advantages: Low risk, mutual complementarity
・Disadvantages: Limited control, profit sharing
Investigation Discovery 3: MECE Application Process
Step 1: Analysis Purpose and Scope Clarification
・What to analyze (analysis target)
・Why to analyze (analysis purpose)
・How far to analyze (analysis scope)
Step 2: Appropriate Perspective Selection
・Classification axis selection suitable for analysis purpose
・Multiple perspective consideration and comparison
・Decision on perspective leading to most insights
Step 3: Element Identification and Classification
・Brainstorming-style element extraction
・Classification by selected perspective
・Gap and overlap checking and correction
Step 4: Detailed Analysis of Each Element
・Deep-dive analysis of each classified element
・Inter-element relationship and priority consideration
・Quantitative data validation
Step 5: Insight and Conclusion Derivation
・Insight extraction from analysis results
・Action and recommendation formulation
・Stakeholder reporting and sharing
The Power of MECE - Hidden Truths
Alert File 1: Prevention of Thinking Gaps Systematically prevents "oversights" when facing complex problems. Enables comprehensive analysis by structuring and grasping the whole, significantly reducing risk of missing important elements or perspectives.
Alert File 2: Dramatic Analysis Efficiency Improvement Eliminates redundant analysis work, achieving maximum analysis effect with limited time and resources. Prevents waste of "already analyzed" or "analyzed from different perspective," promoting efficient problem-solving.
Alert File 3: Logical Persuasiveness Enhancement MECE-based analysis results have high logical consistency, becoming powerful weapons for stakeholder explanation and persuasion. Enables clear demonstration of logical basis for "why that conclusion was reached."
Alert File 4: Common Understanding Promotion Within Teams Unifying analysis frameworks through MECE prevents recognition gaps among team members. Enables discussion on same ground, promoting constructive opinion exchange and decision-making.
Limitations and Cautions of MECE - Potential Dangers
Alert File 1: Mechanical Classification Trap Most frequent problem. Cases where satisfying MECE format becomes the goal, losing sight of original analysis purpose and insight generation. Risk of satisfaction with classification itself without considering "why that perspective is important."
Alert File 2: Arbitrariness in Perspective Selection Possibility of perspective bias due to analyst's subjectivity and experience. Risk of reaching completely different conclusions for same problem with different perspectives. Important to verify through multiple perspectives and objective criteria for perspective selection.
Alert File 3: Excessive Subdivision Cases where pursuing perfect MECE leads to unnecessarily detailed classification, making analysis complex and inefficient. Appropriate granularity classification according to analysis purpose is necessary.
Alert File 4: Insufficient Response to Dynamic Changes Risk of overlooking classification validity changes due to time passage or environmental changes by adhering to single-point MECE classification. Continuous review and updates are essential.
Alert File 5: Qualitative Element Neglect Risk of overemphasizing easily quantifiable and classifiable elements while neglecting important but difficult-to-classify qualitative elements. Particularly prone to overlooking human emotions, culture, values.
Applications and Related Methods of MECE - Related Case Files
Related Evidence 1: Integration with Logic Trees
MECE → Logic Tree Foundation:
・MECE decomposition at each hierarchy level
・Problem structuring and cause identification
・Systematic solution organization
・Logical thinking process visualization
Related Evidence 2: MECE Utilization in Existing Frameworks
[3C Analysis](/behind_case_files/articles/X016_3C): Customer, Competitor, Company
4P Analysis: Product, Price, Place, Promotion
SWOT Analysis: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats
PEST Analysis: Political, Economic, Social, Technological
Each framework designed based on MECE principles
Related Evidence 3: Coordination with 5W1H and 5 Whys
5W1H: Who, What, When, Where, Why, How
5 Whys: Why1 → Why2 → Why3 → Why4 → Why5
Structure each question and analysis level with MECE principles
Comprehensive problem analysis and solution consideration
Related Evidence 4: Combination with Data Analysis and Statistics
・MECE classification in segmentation analysis
・Variable selection in regression analysis
・Factor organization in factor analysis
・Grouping in cluster analysis
Related Evidence 5: Application in Presentation and Document Creation
・MECE design of document structure
・Issue organization and message structuring
・Information organization for audience understanding
・Persuasive logical development
Conclusion - Investigation Summary
Final Investigator Report:
MECE represents "the fundamental principle supporting the foundation of logical thinking." The seemingly simple two principles of Mutually Exclusive and Collectively Exhaustive function as powerful thinking technology that accurately structures complex problems and enables efficient analysis and precise insights.
The most impressive aspect of this investigation was MECE's "universality." It functions as the foundation for all business analysis frameworks (3C Analysis, 4P Analysis, SWOT Analysis, PEST Analysis, etc.) and is utilized as a structuring principle in thinking methods like 5W1H and 5 Whys. This is not coincidental but because it represents fundamental laws of information organization optimized for human cognitive capabilities.
The important discovery that MECE's true value lies not in "classifying" but in "generating insights" was also crucial. By eliminating gaps and overlaps, it accurately grasps problem overview, discovers important elements prone to oversight, and derives efficient solutions. This goes beyond mere organization techniques to become a system supporting creative thinking.
However, the "mechanical classification trap" that many people fall into also emerged clearly. Cases frequently occur where satisfaction with meeting MECE format leads to neglecting essential thinking about why that perspective is important and what should be learned from it. MECE is a means, not an end. What matters is what this principle reveals and what value it creates.
The potential for evolution in the digital age is also significant. Technologies for dramatically enhancing and streamlining traditional manual classification are emerging: automatic classification through AI and machine learning, segmentation in big data analysis, dynamic MECE classification through real-time data.
The most important discovery is that MECE functions beyond an "analysis tool" as a "thinking habit." Daily consciousness of MECE principles naturally develops thinking ability to view things structurally, comprehensive perspectives without gaps, and efficient problem-solving capabilities. This represents not temporary skill acquisition but construction of thinking assets that continue generating value throughout life.
Logical Thinking Maxim: "Superior analysis means organizing complex reality comprehensively without gaps or overlaps, deriving essential insights and actionable solutions from it."
Case Closed