ROI【🔏CLASSIFIED CASE FILE】 No. X026 | What is Logic Tree
📅 2025-06-26
🕒 Reading time: 10 min
🏷️ Logic Tree 🏷️ Learning 🏷️ 【🔏CLASSIFIED CASE FILE】
- What is Logic Tree - Case Overview
- Basic Structure of Logic Tree - Evidence Analysis
- Logic Tree Implementation Process - Investigation Methods
- The Power of Logic Tree - Hidden Truths
- Limitations and Cautions of Logic Tree - Potential Dangers
- Applications and Related Methods of Logic Tree - Related Case Files
- Conclusion - Investigation Summary
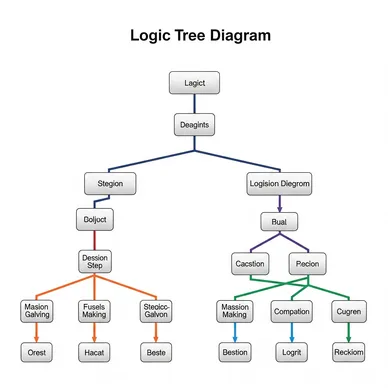
Detective's Note: An analytical methodology demonstrating power in logical thinking and problem-solving - "Logic Tree." This tool decomposes problems and challenges into tree-like structures, organizing thoughts through Why, What, and How frameworks, allegedly possessing the power to see through the essence of complex, intertwined problems and derive accurate solutions. However, reports consistently indicate that many people understand it superficially as "just decompose for now," failing to demonstrate the original power of logical causal relationship construction and effective solution discovery. Why the "tree"? We must uncover the true identity of the logical decomposition mechanism and how hierarchical thinking structures convert complex problems into simple, actionable solutions.
What is Logic Tree - Case Overview
Logic Tree - a logical thinking tool that decomposes and organizes problems or challenges into tree-like hierarchical structures. Systematized in the consulting industry in the 1970s, this methodology is recognized among our clients as an analytical framework that enables identification of root causes and discovery of effective solutions by systematically decomposing complex problems through logical structures of "Why," "What," and "How." However, in actual practice, most companies and individuals use it mechanically as "item enumeration work," unable to fully utilize the original value of logical causal relationship construction and actionable solution development.
Investigation Memo: Problem structuring and solution systematization through hierarchical decomposition. Seemingly simple, yet behind this lies deep thinking technology: "decomposing complex problems into simple elements" and "visualizing logical causal relationships." We must uncover why tree diagrams and the thinking process from decomposition to integration.
Basic Structure of Logic Tree - Evidence Analysis
Primary Evidence: Three Types of Logic Trees
Why Tree (Cause Analysis Type)
Decomposing "why that problem occurred"
・Identifying root causes of problems
・Visualizing causal relationship chains
・Drilling down from surface symptoms to deep causes
・Analysis serving as starting point for problem-solving
Structure Example:
Sales Decline (Problem)
├─ Why? → Customer count decrease
│ ├─ Why? → New customer acquisition decrease
│ │ ├─ Why? → Advertising effectiveness decline
│ │ └─ Why? → Competitor emergence
│ └─ Why? → Existing customer churn
│ ├─ Why? → Service quality decline
│ └─ Why? → Price competitiveness deterioration
└─ Why? → Average spending per customer decrease
├─ Why? → Product unit price decline
└─ Why? → Purchase quantity decrease
What Tree (Element Decomposition Type)
Decomposing "what it consists of"
・Decomposing whole into constituent elements
・Understanding structure and relationships
・Organization without gaps or overlaps (MECE)
・Analysis scope clarification
Structure Example:
Sales (Whole)
├─ Product A Sales
│ ├─ Store Sales
│ │ ├─ Store α
│ │ ├─ Store β
│ │ └─ Store γ
│ └─ Online Sales
│ ├─ Proprietary E-commerce
│ └─ Mall Stores
├─ Product B Sales
└─ Product C Sales
How Tree (Solution Development Type)
Decomposing "how to achieve"
・Systematizing methods and means for goal achievement
・Concretizing and detailing solutions
・Hierarchical organization of execution plans
・Action plan construction
Structure Example:
Sales Improvement (Goal)
├─ How? → New customer acquisition
│ ├─ How? → Digital marketing enhancement
│ │ ├─ How? → SEO measures
│ │ ├─ How? → Social media advertising
│ │ └─ How? → Content marketing
│ └─ How? → Sales activity enhancement
│ ├─ How? → Sales personnel increase
│ └─ How? → Sales skill improvement
├─ How? → Existing customer development
└─ How? → Product unit price improvement
Evidence Analysis: The brilliance of Logic Tree lies in visualizing the logical thinking process of problem analysis (Why) → current state understanding (What) → solution planning (How), enabling systematic problem-solving while preventing gaps and overlaps at each stage.
Logic Tree Implementation Process - Investigation Methods
Investigation Discovery 1: Concrete Logic Tree Application Example (Sales Performance Improvement)
Case Evidence (B2B Sales Department Issue Resolution):
Phase 1: Cause Analysis through Why Tree
Problem: Sales performance stagnant at 70% of target
1st Layer "Why is performance stagnant?"
├─ Few deals
├─ Low closing rate
└─ Small deal size
2nd Layer "Why are there few deals?"
├─ Insufficient new business development
│ ├─ Few appointments secured
│ ├─ Insufficient prospect lists
│ └─ Insufficient sales activity time
├─ Few referrals from existing customers
└─ Few inquiries from marketing
3rd Layer "Why are appointment numbers low?"
├─ Insufficient approach volume
├─ Ineffective approach methods
└─ Insufficient sales approach skills
Root Cause Identification:
・Sales skill deficiency (especially approach and proposals)
・Lack of efficient sales process establishment
・Inadequate marketing coordination
Phase 2: Current State Understanding through What Tree
Sales Activity Component Decomposition
Sales Activities
├─ New Business Development
│ ├─ Lead Generation
│ │ ├─ Telemarketing
│ │ ├─ Email sales
│ │ └─ Referral acquisition
│ ├─ Business meetings
│ │ ├─ Initial meetings
│ │ ├─ Proposals and presentations
│ │ └─ Closing
│ └─ Follow-up
├─ Existing customer development
└─ Sales support tasks
Phase 3: Solution Planning through How Tree
Goal: Achieve 100% of sales target
Solution Systematization:
Sales Performance Improvement
├─ Skill Enhancement
│ ├─ Sales training program implementation
│ │ ├─ Approach skill training
│ │ ├─ Presentation training
│ │ └─ Closing training
│ ├─ OJT and mentor systems
│ └─ External seminar participation
├─ Process Improvement
│ ├─ Sales flow standardization
│ ├─ Thorough CRM utilization
│ └─ Business meeting management enhancement
└─ Organizational structure review
├─ Sales-marketing coordination enhancement
├─ Sales support system enhancement
└─ Evaluation system and incentive review
Investigation Discovery 2: Logic Tree Creation Process
Step 1: Problem and Goal Clarification
・Clear definition of analysis target
・Identification of problems to solve and goals to achieve
・Analysis purpose and goal setting
Step 2: Appropriate Tree Type Selection
・Why: When cause analysis is needed
・What: When current state understanding and element organization is needed
・How: When solution and execution method examination is needed
Step 3: First Layer Element Extraction
・Decomposition based on MECE principles
・Element identification through brainstorming
・Prioritization by importance and impact
Step 4: Hierarchical Deep-dive Analysis
・Further detailed decomposition of each element
・Logical causal relationship confirmation
・Feasibility and reality verification
Step 5: Overall Structure Confirmation and Adjustment
・Logical consistency checking
・Gap and overlap confirmation and correction
・Verification of practical problem-solving applicability
Step 6: Action Plan Development
・Countermeasure planning for identified root causes
・Solution prioritization and execution planning
・Effect measurement and follow-up planning
Investigation Discovery 3: Quality Assurance Checkpoints
Logic Check:
・Are logical connections at each level appropriate?
・Are causal relationships clear and persuasive?
・Is the process leading to conclusions logical?
Comprehensiveness Check:
・Are there no overlooked important elements?
・Is the analysis scope appropriately set?
・Are MECE principles observed?
Practicality Check:
・Is it useful for actual problem-solving?
・Can it be implemented into concrete actions?
・Is the content understandable and relatable for stakeholders?
The Power of Logic Tree - Hidden Truths
Alert File 1: Complex Problem Structuring Organizes complex, intertwined problems into understandable hierarchical structures. Enables both overview of problem scope and detailed analysis. Brings order to potentially confusing situations.
Alert File 2: Logical Thinking Visualization Enables logical verification by externalizing and visualizing mental thinking processes. Discovers thinking leaps and logical contradictions, achieving more accurate analysis and judgment.
Alert File 3: Root Cause Identification Identifies true root causes through systematic drilling down from surface phenomena. Enables fundamental problem-solving rather than symptomatic treatment, with recurrence prevention effects.
Alert File 4: Common Understanding Promotion Within Teams Promotes recognition unification among team members by visualizing logical structures. Enables constructive discussion and efficient decision-making, improving organizational problem-solving capabilities.
Limitations and Cautions of Logic Tree - Potential Dangers
Alert File 1: Mechanical Decomposition Trap Most frequent problem. Cases where decomposition becomes the goal, losing sight of logical causal relationships and practical problem-solving applications. Risk of satisfaction with formal analysis without reaching essential insights.
Alert File 2: Linear Thinking Limitations In complex real-world situations, factors often interact mutually, but tree structures can only express linear causal relationships. Risk of overlooking systemic and circular relationships.
Alert File 3: Analyst Perspective and Experience Bias Decomposition content may be biased by creator's knowledge, experience, and values. Risk of overlooking important factors or analysis results biased toward specific perspectives.
Alert File 4: Excessive Detailing Cases where pursuing perfect analysis leads to unnecessarily detailed decomposition, making analysis complex and inefficient. Risk of decreased execution due to "analysis fatigue."
Alert File 5: Static Analysis Constraints Confined to single-point analysis, unable to capture factor and relationship changes due to time passage or environmental changes. Continuous review and updates are essential.
Applications and Related Methods of Logic Tree - Related Case Files
Related Evidence 1: Integrated Use with MECE
MECE Principles × Logic Tree:
・Thorough MECE decomposition at each level
・Logical structure without gaps or overlaps
・Analysis accuracy improvement and efficiency
・Persuasive logical development
Related Evidence 2: Comparison and Coordination with 5 Whys
5 Whys: Single-line, linear cause drilling
Logic Tree: Multi-faceted, structural decomposition
Selective use and combined application of both methods
Simple problems → 5 Whys, Complex problems → Logic Tree
Related Evidence 3: Coordination with SWOT and 3C Analysis
Strategic Analysis → Logic Tree Development:
・Detailed decomposition of each SWOT element
・Structured analysis of each 3C Analysis element
・Logical foundation construction for strategic planning
・Bridge from analysis to execution
Related Evidence 4: Combination with TOC and AARRR Model
TOC: Constraint identification → Logic Tree for cause analysis and solution planning
AARRR: Issues at each stage → Logic Tree for factor decomposition
Integrated use of problem discovery and analysis methods
Related Evidence 5: Application in Presentations and Reports
・Logical document structure design
・Persuasive logical development
・Clear organization of complex content
・Effective explanation to stakeholders
Conclusion - Investigation Summary
Final Investigator Report:
Logic Tree represents "the culmination of thinking technology that visualizes logical thinking and decomposes complex problems into solvable elements." Hierarchical decomposition through three fundamental questions—Why, What, and How—functions as a powerful tool enabling more systematic and comprehensive analysis while following natural human thinking processes.
The most impressive aspect of this investigation was Logic Tree's "thinking externalization" effect. By organizing complex problems that tend to confuse the mind into visible tree diagrams, logical verification and correction become possible. This prevents thinking leaps and logical contradictions, achieving more accurate analysis and precise judgment.
The comprehensiveness covering the entire problem-solving process also emerged as an important characteristic. The sequential flow of cause analysis through Why Tree, current state understanding through What Tree, and solution planning through How Tree enables consistent logical approaches from problem discovery to resolution.
Through all 26 classified files in the ROI Detective Agency series, it became clear that Logic Tree functions as the foundation for many frameworks. Structuring principles through MECE, deep-dive analysis through 5 Whys, strategic analysis through SWOT and 3C Analysis—various methodologies utilize Logic Tree's logical structures.
However, the "mechanical decomposition trap" that many people fall into also emerged clearly. Cases frequently occur where decomposition itself becomes the goal, losing sight of logical causal relationship construction and practical problem-solving applications. Logic Tree's true value lies not in "decomposing" but in "understanding essence through decomposition and deriving effective solutions."
The potential for evolution in the digital age is also significant. Mind mapping software, AI-assisted logical structure analysis, big data-powered factor analysis—technologies dramatically advancing traditional hand-drawn trees are emerging.
The most important discovery is that Logic Tree functions beyond an "analysis tool" as a "logical thinking habit development system." Habitual thinking through Why, What, and How structures naturally improves logical thinking ability, problem-solving capability, and communication skills. This represents not temporary skill acquisition but construction of thinking assets that continue generating value throughout life.
【ROI Detective Agency Classified File Series Complete】
Through investigations across 27 classified files from X000 to X026, the complete picture of thinking frameworks in modern business has been revealed. From ROI at the beginning, through basic methods like KPT, SWOT, and PDCA, to modern methodologies like AARRR and Lean Canvas, a complete arsenal of business strategy and problem-solving weapons has been assembled.
These frameworks function not as individual tools but as integrated thinking systems that interconnect with each other. By selecting and combining appropriate frameworks for every phase—from analysis through strategic planning, execution, and improvement—reliable results creation becomes possible.
Logical Problem-Solving Maxim: "Even complex problems can always be reduced to solvable elements when decomposed with appropriate logical structures."
Case Closed
Solve Your Business Challenges with Kindle Unlimited!
Access millions of books with unlimited reading.
Read the latest from ROI Detective Agency now!
*Free trial available for eligible customers only